The number of people suffering from hunger has been increasing over the last five years and eventually reached 690 million in 2020. Most of the world is still not on track to achieve the Zero Hunger target by 2030 and the most affected regions, in terms of hunger prevalence, are Asia and Africa. The COVID-19 pandemic is expected to greatly increase the level of hunger worldwide affecting even those regions that have been traditionally more food secure. This article provides a general overview of the current facts and statistics related to world hunger.
Sustainable Development Goals and World Hunger
Back in 2015, the United Nations (UN) launched the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development which comprised 17 interlinked objectives designed to end poverty, protect the planet and achieve prosperity for all. Goal 2 of the Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) agenda relates to Zero Hunger and aims to ensure easy access to safe, nutritious, and sufficient food for everyone while eradicating all forms of malnutrition. Although the last few decades saw the rates of hunger decline steadily, nevertheless since 2015 those levels began to increase again reaching 690 million people in 2020 or 60 million more than in 2015. The UN has warned that if the current trend continues, the number of people affected by hunger could surpass 840 million by 2030.
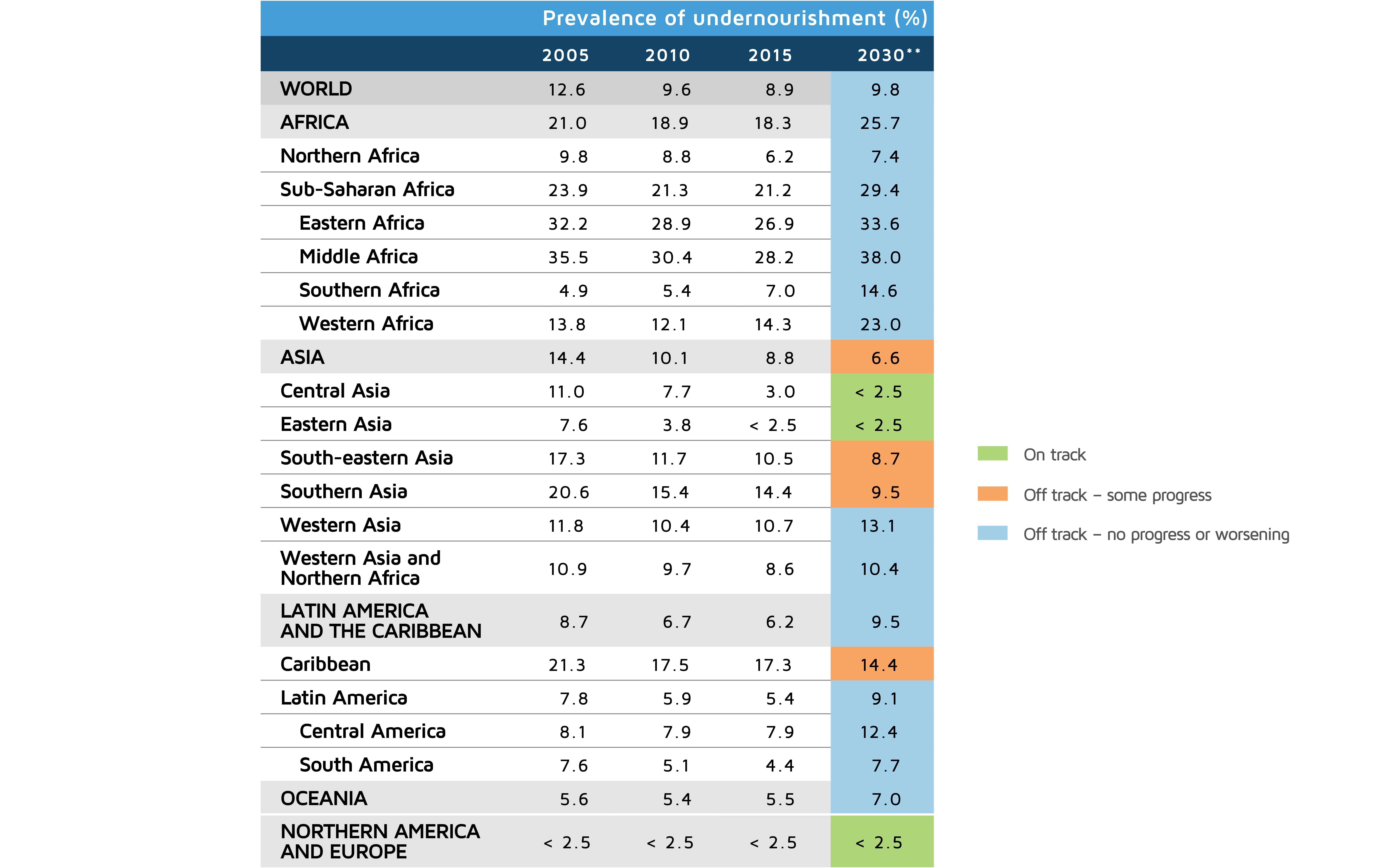
In terms of geographical concentration, the largest number of people suffering from undernourishment is in Africa. In 2019, about 19.1% of the African population was affected by some form of hunger or malnutrition which is 0.8% more than in 2015 while the prevalence of undernourishment in Asia hit 8.3%, or 0.2% less than in 2015. However, some regions in Central and Eastern Asia are on track to reach the 2030 Zero Hunger targets by maintaining hunger levels at around 2.5%.
Fig. 1. Percentage of people suffering from undernourishment
World Hunger Facts and Statistics
- Around 135 million people suffer from acute hunger as a result of conflicts, climate change, and economic turbulence
- In 2019, about 2 billion people did not have access to safe, nutritious, and sufficient food
- In 2019, about one in ten people worldwide, or 750 million overall, were exposed to severe levels of food insecurity
- An additional 130 million people could be at risk of suffering acute hunger as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic
- In 2019, there were over 191 million children under five years of age suffering some form of impaired growth and development due to poor nutrition
- Between 2018 and 2019, the gender gap of those suffering from acute hunger increased with women being more prone to experiencing food insecurity
- About 57% of people living in sub-Saharan Africa and Southern Asia cannot afford a healthy diet
Pathways to Zero Hunger
In order to improve the current situation in terms of hunger prevalence, the UN has suggested a number of policy recommendations designed to provide a comprehensive and integrated transformation. These relate to:
- Transition to sustainable food systems so that the ability of future generations to generate safe and nutritious food is not compromised
- Prioritizing policies aiming to end rural poverty by supporting small-scale producers to increase their income, productivity, and general wellbeing
- Implementation of ‘all food systems’ that will minimize or eliminate food waste during production, storage, and transportation
DevelopmentAid is the leading provider of business intelligence and recruitment tools designed to assist those active in the development sector. Join today and gain access to exclusive information on the upcoming funding opportunities (tenders and grants) from the largest bilateral and multilateral donors.

