The Earth’s population is continually increasing as is the gap between the wealthy and the poor.
People who are born into poor families have little chance of evading poverty according to researchers. Moreover, even those who do manage to find work cannot guarantee that they and their families will have satisfactory living conditions.
Poverty is a term that characterizes an individual’s or a society’s lack of sufficient financial means and necessities to achieve a basic standard of living.
See also: Poverty reflected on the plate
Besides hunger and lack of shelter, the World Bank describes poverty as being the unavailability of work, the lack of freedom, and uncertainty about the future. Today nearly 700 million people live below the poverty line.
Fig.1. The age profile of the global poor by region
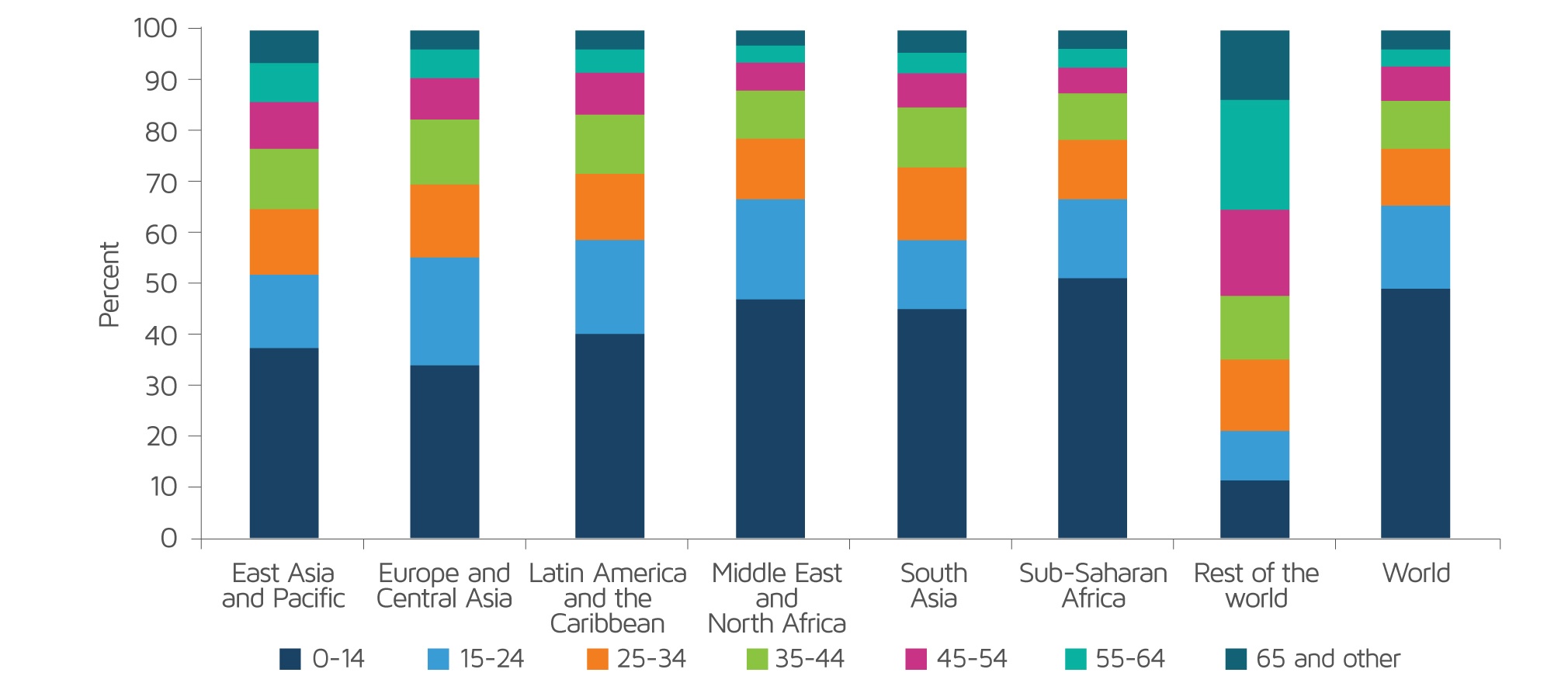
Source: Poverty and Shared Prosperity 2020: Reversals of Fortune
Poverty can be quantified as being absolute and relative.
What is absolute poverty?
The term “Absolute poverty” was described at the World Summit for Social Development back in 1995 as a severe insufficiency of essential human needs (food, drinking water, sanitary conditions, proper healthcare, shelter).
It is worth mentioning that over the last couple of decades the level of poverty around the globe has registered a decrease of 25%. However, the COVID-19 crisis has slowed down this decrease and the numbers are now climbing again.
See also: Pandemic exposes structural inequalities leading to higher poverty rate
According to research from the UN University World Institute for Development Economics Research, the consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic could lead to an increase in global poverty of up to 500 million people.
Sub-Saharan Africa is the region with the highest number of people living in absolute poverty. This is mainly because of various conflicts as well as the effects of climate change which involve extreme temperatures, abnormal precipitation, and natural calamities that leave people without shelter and/or food every year and cause substantial and costly economic damage.
Fig.2. Extreme poverty, 2015-2021
Source: World Bank
Although the number of births per year in African countries has decreased, it nevertheless remains the highest in the world and this trend will continue until at least the end of the 21st century. This means that Africa is at risk of becoming the continent with the highest concentration of people living in absolute poverty.
A 12-year-old who has never seen a doctor or attended school is an illustration of absolute poverty.
Another troubling fact is that a job cannot guarantee a fair livelihood since in 2018, 8% of employed individuals and their relatives were living in poverty.
What is relative poverty?
The term relative poverty refers to situations in which certain people are unable to actively engage in society and profit from activities and events that other people take for granted. These people cannot afford to sustain the average standard of life in the society in which they reside.

It also evolves overtime in that as a society’s wealth increases so does the income that society considers to be sufficient to afford adequate living conditions. Thus, relative poverty depends on the society in question.
For example, back in 1963, in order for a US family of four to live above the relative poverty level, it needed an income of over US$3,100 a year. By 1992, the figure had risen to US$14,228 and in 2020, an income of less than US$40,500 per year would throw a family into relative poverty while the median household income in the country has reached US$67,521.
See also: One in seven Americans to have resources below poverty rate in 2021
Poverty is an issue that is being addressed by most of the world’s development organizations in their efforts to eradicate it. Despite the significant progress made over the last several decades, the COVID-19 pandemic has slowed progress down although the international development community remains univocal in its fight against poverty. Eradicating this phenomenon is a complex process that requires structural reforms and significant funding.

