Genetically Modified Organisms, also known as GMOs, are plants, animals, or other living organisms that have undergone some kind of genetic modification. These are used to improve crop yields or to enhance specific characteristics of plants and animals. Currently, there are strongly opposed views on the safety and applicability of GMOs with two distinct camps clashing on the potential benefits and drawbacks. This article defines GMOs, presents certain areas for potential application, and highlights those countries that have banned the use of genetically modified organisms.
What are GMOs?
Genetically Modified Organisms or GMOs refer to plants, animals, or other living organisms that have undergone some sort of genetic modification generated by genetic engineering or transgenic technology.
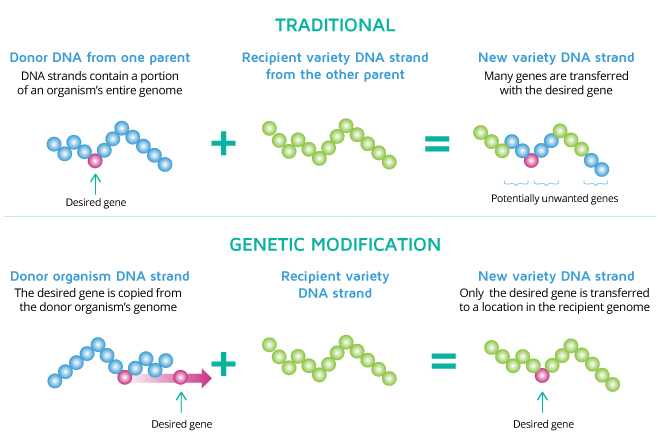
While GMOs are similar to traditional selective breeding, mechanisms are used for the direct insertion of genetic material rather than relying on natural selection processes based on sexual and asexual reproduction.
The technology was introduced to address the drawbacks of traditional breeding that often yielded offspring that lacked the desired gene or resulted in other undesirable traits. It targets only the specific genes that are inserted in the recipient DNA, producing offspring possessing only the required traits.
🔹 Examples of GMO applications:
- Genetic modifications in crops to improve yield, quality, nutritional aspects, or resistance to disease and pests (e.g., rice modified with daffodil genes to produce beta-carotene)
- Genetic modifications in microorganisms to create desired chemical substances for pharmaceutical or energy purposes (e.g., insulin, ethanol, biodiesel)
- Genetic modifications in animals to enhance specific traits (milk production, disease resistance) or to produce human transplant tissues and organs
Fig.1. Types of plant breeding (GMO vs Traditional)
GMOs and the environment
The influence of GMOs on the environment is multiple and it depends on the perspective used to study the issue.
Some stakeholders highlight the benefits that GMOs bring to the environment while others point out the alarming environmental concerns. It is worth mentioning that both camps have a strong presence and convincing arguments.
🔹 Why are GMOs good for the environment?
- One study on genetically modified crops has shown that the adoption of these in crop production may decrease the use of insecticides and thus prevent bees and other pollinators being poisoned
- By using herbicide-tolerant crops, farmers do not need to till the soil to get rid of weeds which in turn maintains soil health and reduces fuel and labor use
- GMO crops increase food security and lower the pressure on the environment. Moreover, consumers have access to food that is more affordable.
🔹 Why are GMOs bad for the environment?
- The biggest concern in relation to GMOs is the phenomenon of pleiotropy which occurs when the alteration of one gene influences two or more seemingly unrelated traits. Thus, changing one element in the DNA may lead to alterations in the organism’s nutritional, toxic and allergenic properties
- While GMOs are often engineered to be herbicide-resistant, the use of chemicals to eradicate noxious weeds leads to the harmful residues being spread to the surrounding ecosystems
- Active use of GMOs is shown to contribute to the formation of superweeds that are resistant to herbicides
Current stance on GMOs
The debate on the safety and applicability of GMOs has evolved in the political world. Several countries support a strong negative narrative towards the use of GMOs while other states ensure that public opinion regarding GMOs is that they are safe for human, plant, and animal health. It is worth mentioning that despite a negative stance, some countries allow the growth or import of certain GMO species.
🔹 Which countries have banned GMOs?
- European Union: France, Germany, Austria, Greece, Hungary, the Netherlands, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Bulgaria, Poland, Denmark, Malta, Slovenia, Italy, and Croatia
- Other European countries: Switzerland, Russia
- Asia-Pacific: Australia, Turkey, Kyrgyzstan, Bhutan, Japan, and Saudi Arabia
- Africa: 43 countries in Africa have banned (partially) the growth of GMOs
- Americas: Belize, Ecuador, Mexico, Peru, and Venezuela.
🔹 Countries that allow GMOs
- European Union: the Flemish region of Belgium and Romania
- Other European countries: the United Kingdom
- Asia-Pacific: China, India, and Pakistan
- Africa: Burkina Faso, Sudan, South Africa, and Nigeria
- Americas: The USA, Canada, Brazil, and Argentina
See also: UK seeks deregulating gene-edited crops
The growth and use of GMOs is a hot topic in many countries. While there is an acute need to develop plants and animals that bring higher yields and can withstand the severe conditions caused by climate change, it is unclear if GMO technology is the right answer. There are two distinct camps that have opposing views on the effects that GMOs have on the environment. More research is necessary before we decide to ban or apply this technology for mass production.
DevelopmentAid is the leading provider of business intelligence and recruitment tools designed to assist those active in the development sector. Join today and gain access to exclusive information on upcoming funding opportunities (tenders and grants) from the largest international donors.