An increasing number of people around the world face serious health issues due to inadequate nutrition, poor access to healthcare and sanitation, and water scarcity. These conditions, when combined with certain geographical and biological criteria, offer a perfect environment for tropical diseases to spread. Dengue fever, Brazilian spotted fever, Chagas disease are just a few of a group of 20 neglected tropical diseases that can have a serious impact on human lives, societies and even international development. However, these diseases are largely ignored by international financial organizations.
Neglected tropical diseases predominantly affect those facing poverty and a lack of proper sanitation. Insect bites and contact with polluted water and soil are two of the main contamination causes. Together with worsening health, NTDs can cause physical malformations, disability, and stigma which can then lead to isolation from society.
Furthermore, NTDs can restrict adults and young people from acquiring knowledge and growing to their maximum potential to help their families and communities which has negative societal and economic effects.
What are neglected tropical diseases?
NTDs represent a diverse group of 20 diseases that are primarily found in tropical regions where they affect over 1 billion individuals worldwide. For the most part, these are caused by pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites as well as toxins.
NTDs have a negative impact on a person’s cognitive and physical growth, reduce productivity and significantly increase morbidity and death, particularly among people who live in some of the poorest regions on Earth.
People who are typically impacted by NTDs are those who have to face a variety of problems on a daily basis, including poverty, poor sanitation, and exposure to infectious vectors and livestock.
List of some of the NTDs, and where they come from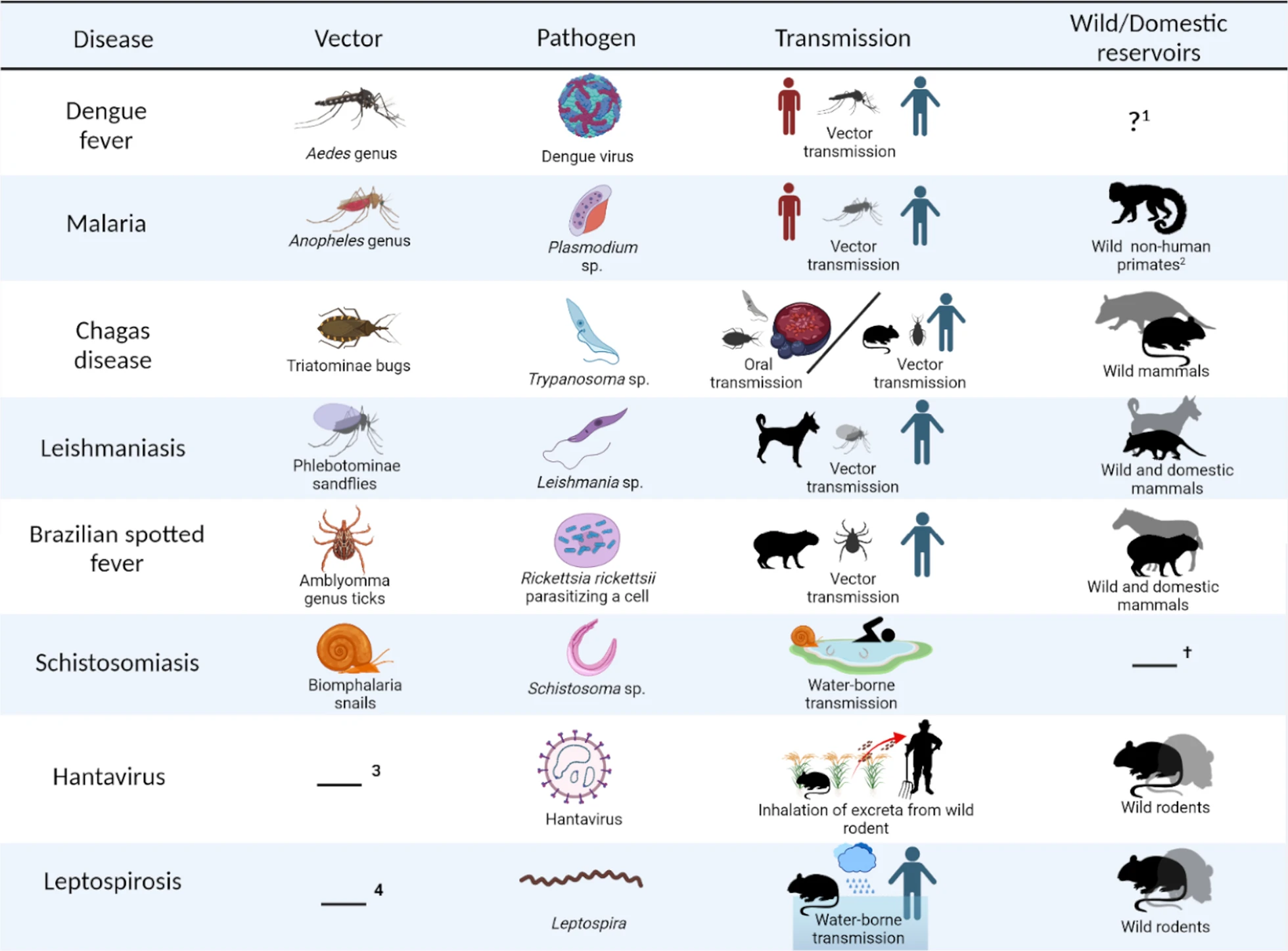
Source: BMC
Why is this group of diseases dubbed ‘neglected’?
The answer is quite simple – the global health agenda barely makes any mention of them (hence neglected). The World Health Organization outlines that the NTDs are virtually completely ignored by international financing organizations.
These diseases affect populations from low-income countries with high poverty rates. NTDs impact not just adults, but children as well, contributing to the marginalization of infected children and thus impacting their academic performance. Adults face limited career options and, just like children, have to deal with social marginalization.
Neglected tropical diseases statistics
The following information on NTDs was provided by the World Health Organization:
- Despite the fact that at least one case of NTD was identified in 179 nations and regions in 2021, 16 nations accounted for 80% of the worldwide NTD burden
- As of the end of 2022, 47 nations had already eradicated at least one NTD, and more were on track to do the same
- Yearly, in the period 2016-2019, over one billion people underwent treatment for NTDs
- In 2021, 1.65 billion individuals were estimated to need mass or individualized care and therapy for NTDs which is about 25% less compared to 2010 when the figure was 2.19 billion.
The impact of NTDs on international development
One well-known and significant factor influencing NTDs is socio-economic fragility. For instance, parasite transmission may be impacted by poverty and poor sanitation. In addition, NTDs typically have an adverse effect on labor productivity.
NTDs affect children’s opportunities for learning by causing problems with cognitive development and having negative consequences on academic performance and overall development. Furthermore, NTDs such as Lymphatic Filariasis (LF) lock people in a cycle of poverty, resulting in social stigma.
Other NTD-related diseases such as Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF) demand urgent treatment which is very expensive. While timely immunization aids a reduction in rabies transmission, the vaccine is still costly and, in some cases, it is simply unavailable, particularly in the sub-Saharan region.
Needless to say, when people (particularly in low-income countries) stop working, agricultural output suffers, reducing family income and contributing to malnutrition.
Which country faces the worst effects of NTDs?
One research has shown that Nigeria and 15 other nations carry the highest burden of NTDs.
According to the World Population Prospects 2022 report by the United Nations, eight nations will account for over 50% of the increase in the world’s population over the next 30 years: the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, India, Nigeria, Pakistan, the Philippines, and the United Republic of Tanzania.
The situation is particularly serious for Nigeria which is home to 25% of all Africans who are afflicted by NTDs. According to estimates, 165 million residents (over 80% of the country’s population) require NTD treatment as of today.
Data shows that NTD-affected school-aged children could potentially lose up to US$7.2 billion in lost earnings if they fail to receive the necessary care.
Assuming NTD eradication is accomplished by 2030, the Nigerian economy stands to gain US$18.9 billion from its population’s higher productivity by then. The country can still benefit from these gains even after 2030 since people who are cured will lead more successful and satisfying lives.
How are NTDs and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) connected?
NTDs are most important for SDG 3 – Good Health and Well-being. The SDG Target 3.3 “Communicable diseases” can be directly achieved as a result of actions taken against NTDs. This goal, among others, aims to deal with NTD epidemics by 2030.
Numerous other SDGs, including 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, and 17, are indirectly impacted by NTD actions, and successes with some SDGs, including 6, 9, 11, and 13, are essential to combating NTDs.
Final word
Today, an astonishing number of individuals are afflicted by neglected tropical diseases which have a profound impact on entire populations and the growth of their countries’ economies. Infected people may face stigmatization, and be forced to live without sufficient financial resources and thus be unable to help their families and communities. Children with NTDs lack proper education and, without investing in the future, a country simply cannot prosper. International organizations are paying more and more attention to this problem which is one of the reasons why the UN has included NTDs in its Social Development Goals. Some countries have managed to eradicate at least one NTD and, with proper investments and actions taken to eliminate this group of diseases, many nations will be able to solve numerous societal and economic issues.

