Countries around the world progress at different rates due to various geographical, historic, or political factors. One way to categorize this progress is based on the stages of the countries’ socio-economic development and the classification proposed by the United Nations (UN) can be used to achieve this. Thus, the UN distinguishes three distinct groups of countries, specifically developed, developing, and Least Developed Countries (LDC).
What are Least Developed Countries?
Based on the UN definition, Least Developed Countries represent a group of developing countries that exhibit a range of socio-economic and environmental indicators below or above the pre-established benchmarks. Those countries show low levels of human assets, are highly vulnerable to economic and environmental shocks and face a number of severe structural barriers to sustainable development. As of 2021, the UN distinguishes 46 LDC spread across four continents with 33 countries in Africa, nine in Asia, three in Oceania, and one in Latin America and the Caribbean region. In the last two decades, five countries have graduated from the LDC list with Botswana graduating in December 1994, Cabo Verde in December 2007, the Maldives in January 2011, Samoa in January 2014, and Equatorial Guinea in June 2017.
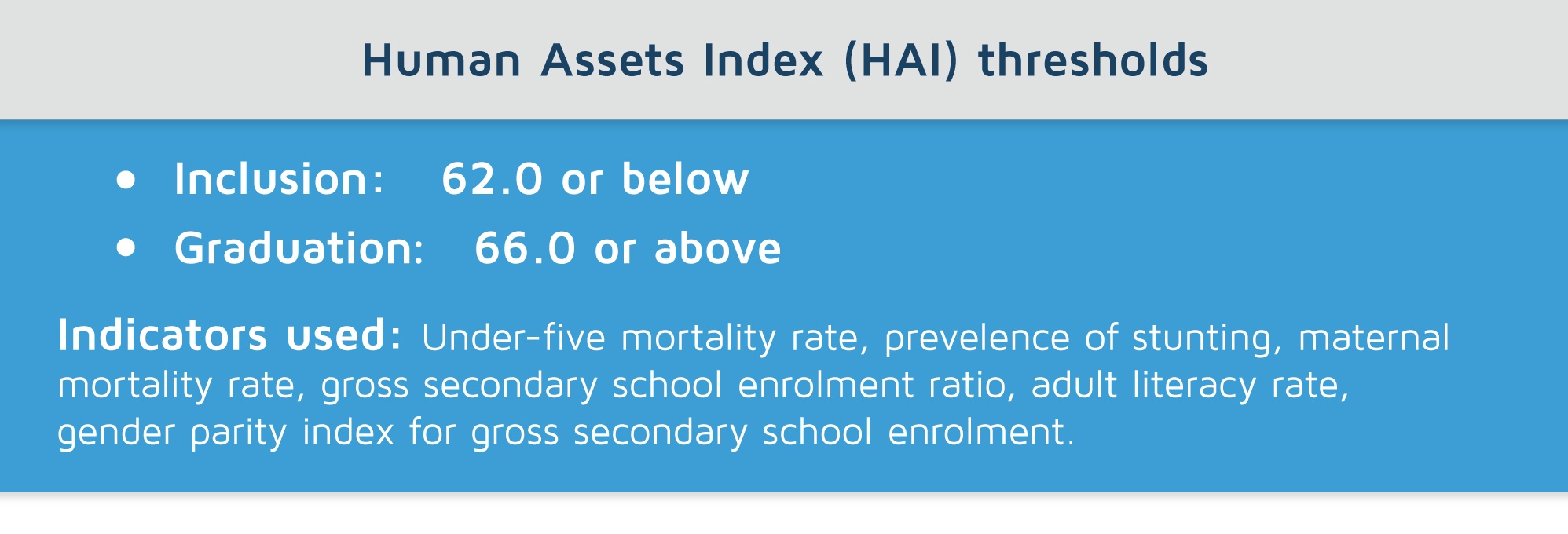
Indicators used for LDC inclusion
In order for a country to be included on the LDC list, it has to meet the inclusion threshold at one triennial review (recurring every three years). The review focuses on three specifically designed indicators that relate to the Gross National Income (GNI) per capita, the Human Asset Index (HAI), and the Economic and Environmental Vulnerability Index (EVI).


Top 10 least developed countries with the lowest income
Somalia was assigned LDC status in 1971. Data from the 2021 review highlights a GNI per capita of only $104. The HAI shows a low value of 24.3, partly influenced by high mortality rates among children under five (117 per 1, 000 children) and maternal deaths (829 per 100,000 women).
Burundi was assigned LDC status in 1971. Based on the latest triennial review (2021), Burundi has a GNI per capita of only $282, significantly lower than the graduation threshold ($1,222). The HAI shows a value of 53.9, partly influenced by a moderate ratio of secondary school enrolment (45.1%) and a moderate rate of adult literacy (68.4%).
South Sudan was assigned LDC status in 2012. Data from the 2021 triennial review shows a GNI per capita of $351. The HAI indicator has a value of only 22.0, influenced by a high rate of maternal mortality (1,150 per 100,000) and by a low rate of secondary school enrolment (11%).
Malawi was assigned LDC status in 1971. Data from the 2021 review highlights a GNI per capita of $367. The HAI has a moderate value of 55.5, somewhat below the graduation threshold (66.0). The EVI value is relatively high (44.5) influenced partly by a moderate share of the population living in drylands (31%).
Mozambique was assigned LDC status in 1988. The latest data shows a GNI per capita of $473. The HAI indicator has a moderate value of 53.9. The EVI value is relatively high (41.4) influenced partly by a moderate share of the population living in drylands (26.2%).
Central African Republic was assigned LDC status in 1975. The latest report shows a GNI per capita of $475. The low value of the HAI indicator (27.4) is caused in part by high mortality rates among children under five (110.1 per 1,000 children) and low rates of secondary school enrolment (17.1%).
Madagascar was assigned LDC status in 1991. Data from the 2021 triennial review shows a GNI per capita of $496. The values for the HAI (60.7) and the EVI (34.8) are nearing graduation levels.
The Democratic Republic of the Congo was assigned LDC status in 1991. The latest review shows a GNI per capita of $506. The HAI indicator value of 47.9 is due partly to the relatively high mortality rates among children under five (84.8 per 1,000 children). However, although DRC has encountered a low value of the EVI – 28.3, nonetheless this is not sufficient to graduate from the LDC list.
Liberia was assigned LDC status in 1990. The latest data shows a GNI per capita of $507. The HAI value of 45.2 is due partly to the relatively high mortality rates among children under five (84.6 per 1,000 children) and maternal deaths (661 per 100,000 women).
Afghanistan was assigned LDC status in 1971. Data from the 2021 triennial review shows a GNI per capita of $513. The HAI value of 42 is due partly to the moderate rates of mortality among children under five (60.3 per 1,000 children) and maternal deaths (638 per 100,000 women). The EVI value is relatively high (44.8) influenced partly by the large share of the population living in drylands (99.0%).
According to the latest report issued by the United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA), the population of underdeveloped countries is more prone to be affected by the consequences of climate change.
DevelopmentAid is the leading provider of business intelligence and recruitment tools for those active in the development sector. Join today to gain access to exclusive information on upcoming tenders and grants, potential partner organizations, short- and long-term projects for individual consultants, tender shortlisting, and awards.

